How to Create Titles for Elective Courses
/
"What are some common titles for elective credit in high school?"
Before titling a course, one must understand the difference between core and elective courses and how these terms are used in the educational world—the "education-eze". Colleges use “education-eze”.
Parents must also understand what is and isn't required by their state school law statutes. Though some colleges and universities hire home education admission personnel versed with knowledge to help homeschooled applicants, other advisors are not always familiar with state statutes, requirements, or procedures. Knowledgeable parents have the means to empower student applicants who may face questions.
Core courses are offerings in the major discipline areas of English, math, social sciences, and natural sciences. Some districts (and colleges) include foreign or world languages in core courses. All other courses are considered electives.
For this post, I am revising an elective list I created in 2015. The list does not include courses most often considered core academics--for example, Calculus or British Literature--though those core courses could also be used as electives if the core course requirements have been meet.
English Electives (when not considered part of the core content English I, English II, English III, and English IV)
Shakespearean Theater
Greco-Roman Theater
Short Stories
Poetry (perhaps of a specific historical era or demographic)
Writing for Print and Publication
Creative Writing
Yearbook
Digital Publishing
Ancient Languages
Biblical Studies: Old Testament
Biblical Studies: New Testament
Communication Electives
Speech (this course may considered a core by some schools)
Competitive Speech
Impromptu Speech
Expository Speech
Policy Debate
Lincoln-Douglas Debate
Media Productions
Mathematics Electives
Business Mathematics (some schools no longer consider this a high school level course)
Personal Finance (this course is often considered a required course for some schools but an elective for others)
Social Science Electives
Comparative Government
Global Studies
International Relations
Introduction to Law
Mock Trial
Constitutional Law
Independent Study: Foreign Policy
Introduction to Criminal Justice
Psychology (this course may be considered a core course for some schools and an elective for others)
Sociology
Anthropology
Archaeology
Family and Consumer Science
Contemporary World Issues
Ancient Civilizations
Independent Study: The Korean War
Medieval History
Introduction to Social Work
Child and Adolescent Psychology
Philosophy
World Religions
Theology
Church History
Internship: Youth Ministry
Natural Science Electives
Environmental Science
Animal and Agricultural Sciences
Introduction to Agriscience
Equine Science
Equine Medicine
Introduction to Veterinary Science
Introduction to Forestry
Botany
Entomology
Zoology
Astronomy
Introduction Aerospace Science
Forensics
Introduction to Health Sciences
Performing/Fine Arts Electives
Introduction to Drama
Musical Theater
Art History (perhaps add a historical era, for example Asian Art History)
Art Appreciation
Choreography
Dance Technique (consecutive years add beginning, intermediate and advanced)
Competitive Dance
Introduction to Ball Room Dance
Stagecraft
Set Design
Theater Production
Two-Dimensional Art
Three-Dimensional Art
Sculpture
Ceramics
Drawing and Painting
Cartooning and Caricature
Printmaking
Pottery
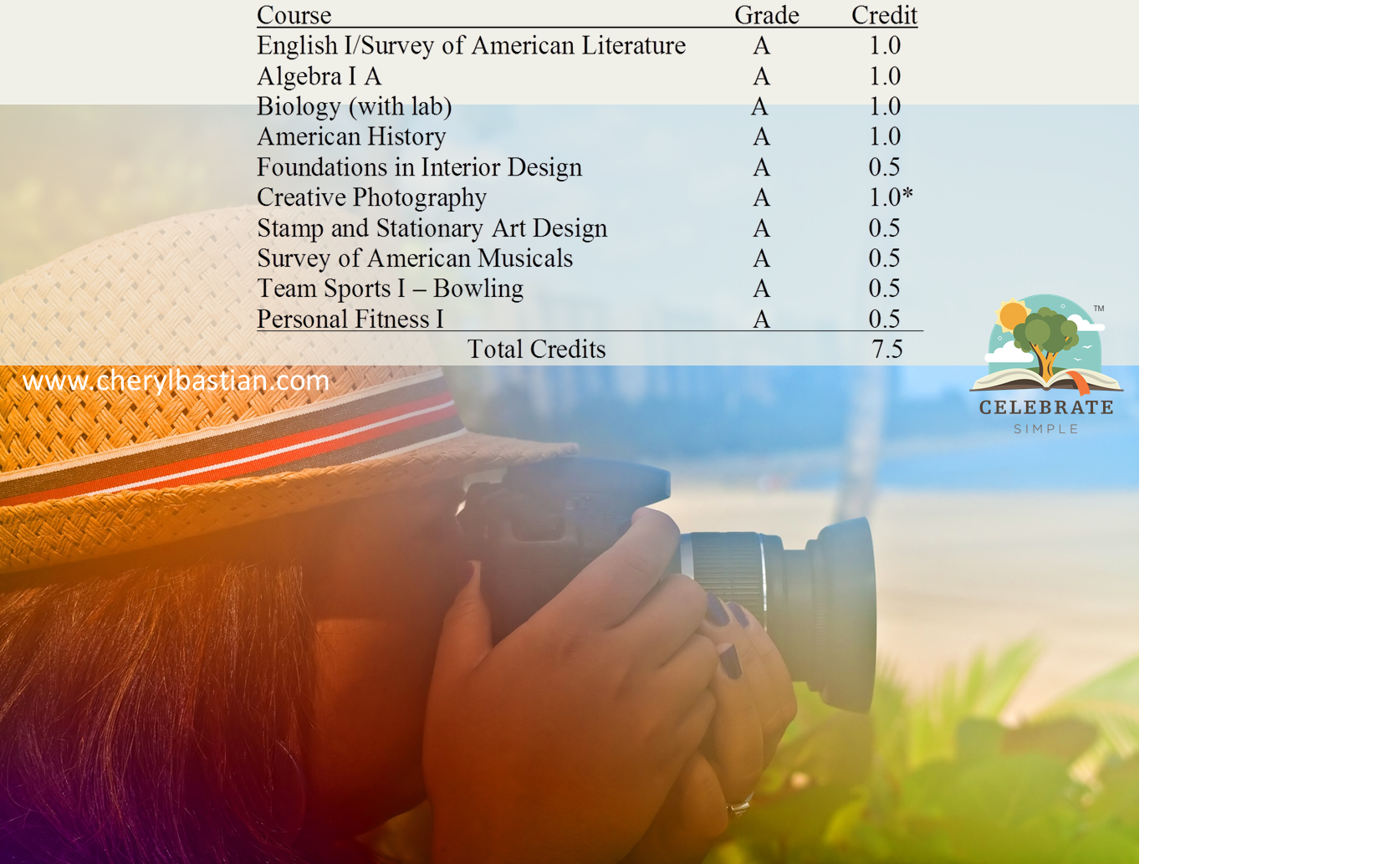
Creative Photography
Digital Photography
Band
Orchestra
Symphonic Band
Wind Ensemble
Jazz Ensemble
Keyboard
Piano
Music Theory (consecutive years add beginning, intermediate and advanced)
Music History (perhaps add a historical era or genre, for example, History of Jazz)
Music Appreciation
Physical Education Electives
Personal Fitness (this course is sometimes considered a required course for some schools but an elective for others)
Nutrition and Wellness
Aerobics
Tennis
Golf
Volleyball
Competitive Swimming
Water Polo
Lifesaving
Advanced Lifesaving
Team Sports
Recreational Sports
Beginning Weights (consecutive years add intermediate and advanced)
Weight Training (often accompanies sports training and play)
Sports Psychology
Introduction to Sports Medicine
Care and Prevention of Athletic Injuries
Sports Rehabilitation
Business Education Electives
Accounting
Marketing
Copyright Law
Advertising and Sales
Principles of Entrepreneurship
Banking and Finance
Business Principles
Foundational Principles of Small Business
Business Technology
International Business
Global Business Studies
Computer Science Electives
Computer Fundamentals and Programming
Introduction to Computer Systems
Computer Design and Repair
Keyboarding
Word Processing
Graphic Design
Digital Design
Web Design
Digital Arts
Computer Gaming
Home Economics Electives
Fashion Design
Textiles and Fabrics
Clothing Construction and Textiles
Machine Sewing
Quilting and Applique
Interior Design
Introduction to Early Childhood Education
Nutrition
Principles in Food Preparation
Principles in Food Preparation: Pastry
Principles in Food Preparation: Desserts
Principles in Food Preparation: Main Courses
Principles in Food Preparation: Appetizers
Introduction to Culinary Arts
Introduction to Pastry
Cake Decorating
Home and Automotive Repair
First Aid and CPR
Emergency Preparedness
Vocational Electives
Cosmetology
Cabinet Making
Carpentry
Trim and Finish Carpentry
Masonry
Landscaping
Horticulture
Floral Design
Landscape Architecture
Building Design and Architecture
Drafting
Technical Drawing
Plumbing
Welding
Auto Mechanics
Diesel Mechanics
Small Engine Repair
Electronics and Circuitry
When our young adults are reading, working on research, studying content, or participating in an experiential opportunity, I search for potential titles. If I can't find a title or course content close to what our learners are studying, I search for high school courses (and in some cases college courses) offered at other high schools across the nation. Those resources usually allow me to find a title--or at least give me a springboard--which accurately describes the content being learned.
If you want to learn more about documentation of elective credits and how to create college admission paperwork, check out this post.
This blog post is intended to offer an example of personal experience. It is in no way intended to be legal advice and should not be taken as such. Parents own the sole responsibility for the training and education of their children.